There is a great deal of uncertainty surrounding the current state of the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program. June 2021 was a pivotal month in the history of the EB-5 program—on June 22, the U.S. District Court of the Northern District of California ruled to invalidate the EB-5 Final Rule. This measure had raised the minimum investment amounts to $900,000 for targeted employment area (TEA) projects and $1,800,000 for non-TEA projects. The court’s ruling caused the minimum investment amounts to return to their pre-November 2019 status of $500,000 for TEA projects and $1,000,000 for non-TEA projects. Of course, these lower amounts were a great incentive for individuals considering an EB-5 investment.
Just a few days later, on June 30, 2021, the regional center program was suspended because the Senate failed to pass the EB-5 Reform and Integrity Act of 2021, which would have reauthorized the program for three more years. As a result, United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) has ceased to process all I-526 petitions associated with a regional center EB5 investment.
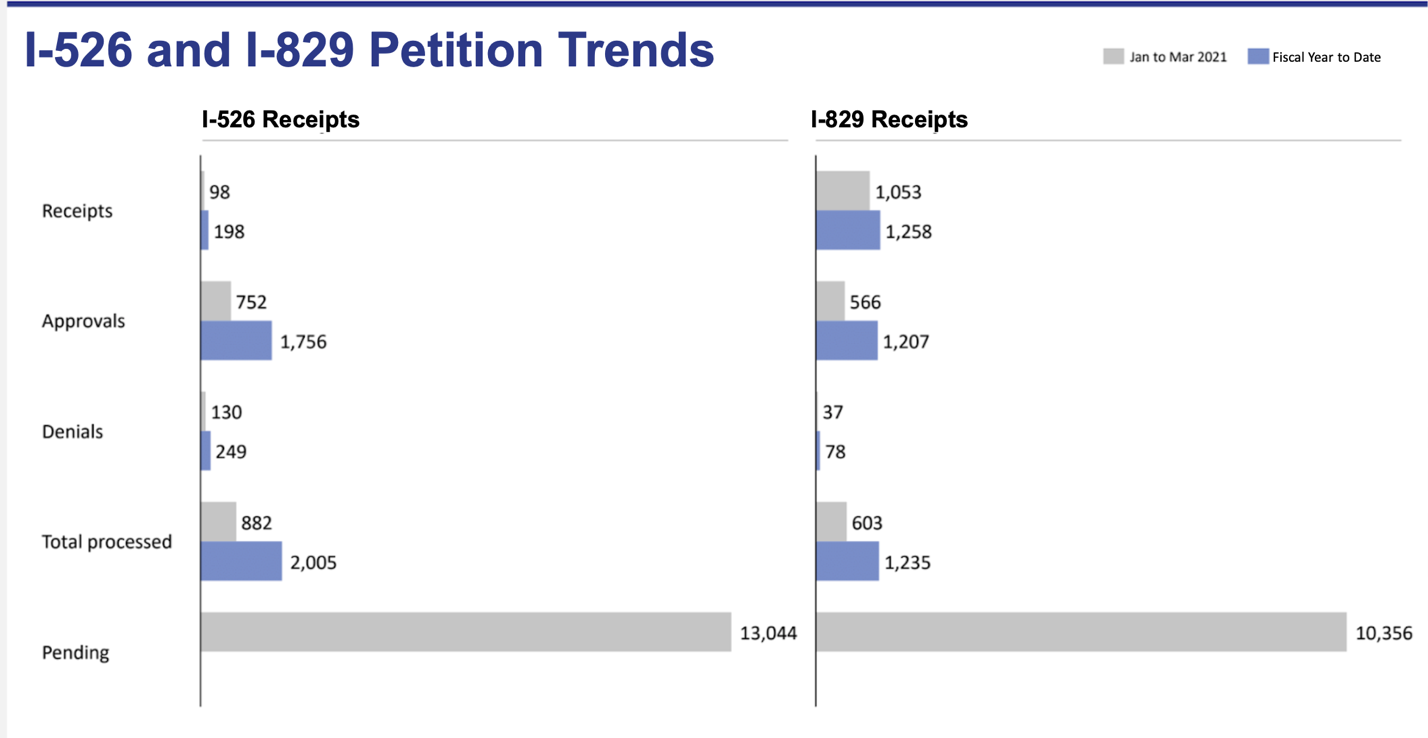
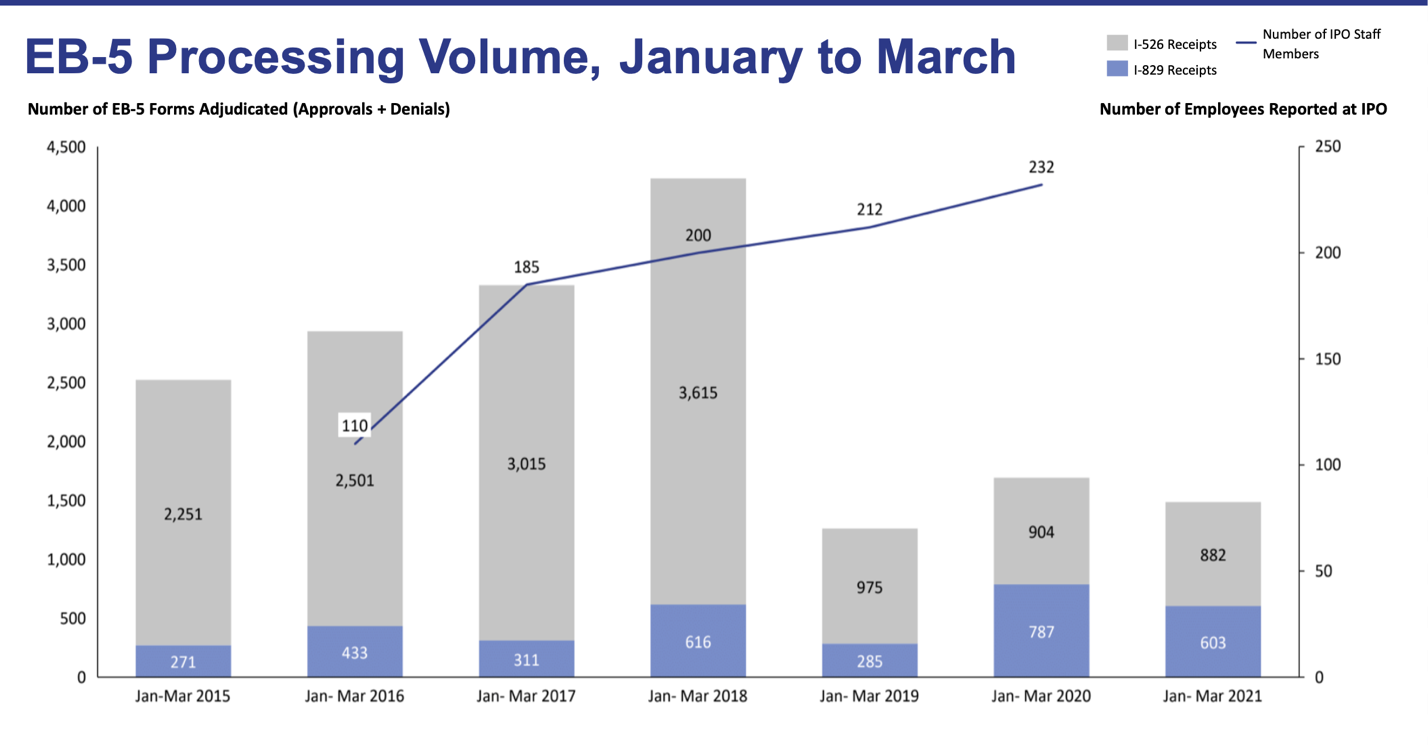
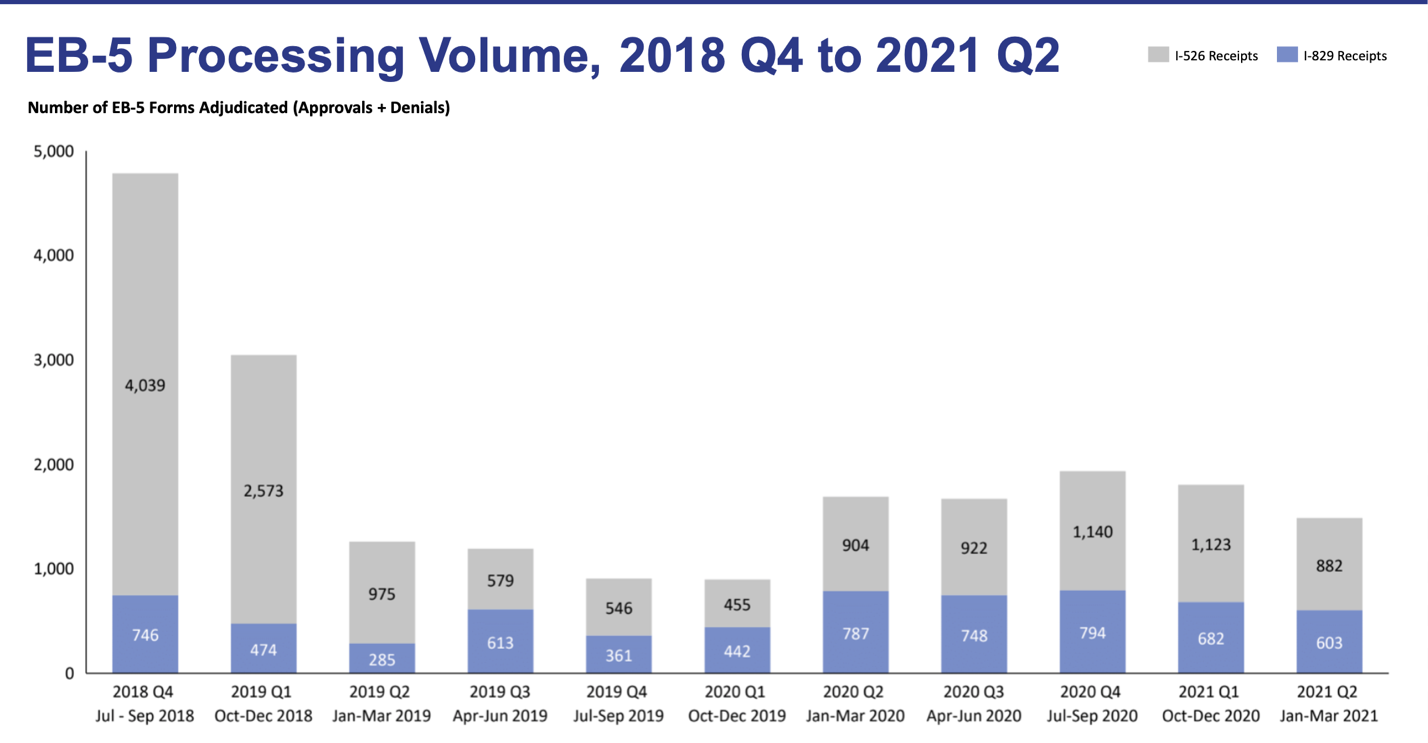
During this tumultuous period for the EB-5 program, USCIS published the processing statistics for January to March 2021 (FY2021 Q2). The number of processed I-526 and I-829 petitions remained remarkably low, which reflects the Immigrant Investor Program Office’s (IPO’s) reduced productivity levels. This trend is especially disappointing in light of the lower demand caused by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic—in theory, USCIS adjudicators should have more time available to take care of incoming petitions. Still, the receipt statistics do show some improvement for Form I-829.
Possible Effects of the Regional Center Program’s Expiration
The processing data shows how urgent and critical it is for the regional center program to be reauthorized by the government. By the end of March, there were over 13,000 unprocessed I-526 petitions. The regional center program’s suspension has undoubtedly caused difficulties for thousands of investors (past data shows that the vast majority of EB-5 investments are made in regional centers).
The regional center program’s inactive status may be good news for direct EB-5 investors and I-829 applicants. Given that USCIS will no longer accept I-526 petitions associated with regional centers, more adjudicators should be available to work on direct EB-5 investment I-526 petitions and I-829 petitions. If this is the case, then the existing backlog of I-526 petitions could be processed in its entirety by the end of 2021. Of course, these are all conjectures—there is no way of knowing exactly when the reauthorization of the regional center program will take place.
On the bright side, the receipt data for Form I-829 is positive when compared to the statistics from the previous quarter: from January to March 2021, there was a total of 1,053 received I-829 petitions. This means that an increasing number of EB-5 investors are completing their conditional permanent residence period and applying for permanent residence. In contrast, only 98 I-526 petitions were received during this period.
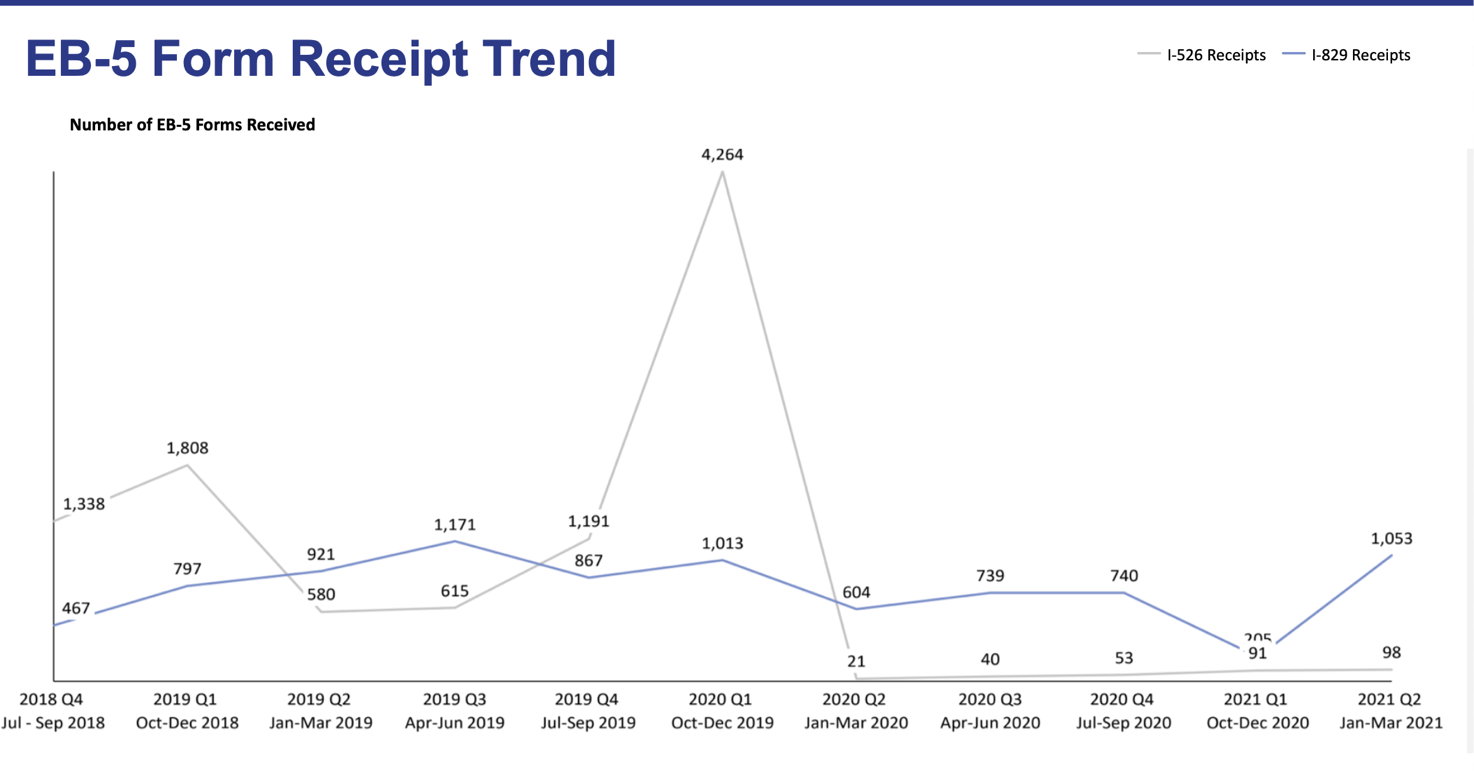
As mentioned, the uncertainty surrounding the regional center program and the EB5 investment minimum amounts makes it difficult to predict what the trends for the following quarter will look like. Nonetheless, investors can be sure that the regional center program will likely be reauthorized in the near future.