
Many foreign nationals seek to live and work in the United States with their families indefinitely. But to make this happen, they first need to gain permanent resident status.
There are several ways of accomplishing this, and for some, the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program presents the easiest and quickest path. The program allows individuals to gain an EB-5 Permanent Resident Card—often referred to as a Green Card—by making a qualifying investment to contribute to economic growth in the United States.
This article explains what the EB-5 visa is and some of the many benefits of gaining an EB-5 Green Card.
A Guide to the EB-5 Program
- 1. Invest in a New Commercial Enterprise
- 2. Apply for the EB-5 Visa
- 3. Apply for a Conditional EB-5 Green Card
- 4. Fulfill EB-5 Program Requirements
- 5. File Form I-829
How Long Does It Take to Get an EB-5 Green Card?
Permanent Resident Status Rights and Responsibilities
Rights of Permanent Residents and U.S. Citizens Compared
Get Your EB-5 Permanent Resident Card with EB5AN
A Guide to the EB-5 Program
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program aims to stimulate economic growth in the United States by attracting foreign investment as a means to create jobs for U.S. workers. In exchange, foreign investors can live and work in the United States, and eventually gain an EB-5 Permanent Resident Card. The program also allows them to gain permanent resident status for their spouse and dependent children.
There are several stages to the EB-5 program, so the entire process of earning an EB-5 Green Card may take several years. However, one of the program’s main benefits is that applicants can live and work in the United States throughout the entire process by gaining conditional permanent resident status.
Here is a brief step-by-step overview of the EB-5 visa process:
1. Invest in a New Commercial Enterprise
Applicants first need to invest at least $800,000 in a new commercial enterprise (NCE) that was established after November 29, 1990, or in a troubled business that they will restructure or expand.
The commercial enterprise must be for-profit. The business can have any management structure, but limited liability companies (LLCs) or partnerships often suit the EB-5 program requirements best.
If the chosen new commercial enterprise is based in a targeted employment area (TEA), the EB-5 visa applicant only needs to invest $800,000. If it is not based in one of these areas, then they must invest $1,050,000.
What Is a TEA?
A targeted employment area (TEA) is an area with:
- A population of fewer than 20,000 people
- An unemployment rate of at least 150% of the national average
There are several benefits to investing in projects located in TEAs, including:
- Lower investment amount ($800,000, compared to $1,050,000 for projects located elsewhere)
- Faster Form I-526 processing
- Reserved visas to help investors avoid visa backlogs
EB-5 applicants can make an investment either directly or via regional centers.
A direct investment is when the individual invests capital directly into the new commercial enterprise. A new commercial enterprise can only have one EB-5 direct investor. In these cases, the EB-5 investor is usually involved in the day-to-day management of the business.
Regional centers, on the other hand, are organizations set up to pool EB-5 funds from several foreign investors, managing the allocation of these funds to the project.
2. Apply for the EB-5 Visa
Next, the individual must apply for the EB-5 visa by submitting Form I-526/I-526E to United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). If the foreign national made their investment via a regional center (as the vast majority choose to do) then they must submit Form I-526E.
An I-526 or I-526E petition should include:
- The individual’s personal information, including full name, date and country of birth, and current address.
- An explanation of how the individual’s investment will meet EB5 program requirements, particularly how it will create at least 10 full-time jobs for U.S. workers.
- Proof of—and details about—their investment in the new commercial enterprise, including a comprehensive business plan.
- Detailed information outlining the lawful source of their investment funds.
- Supporting documentation, including financial and bank statements, property records, tax returns, and more.
Submitting the I-526 petition is a crucial step in the EB 5 process, and it can be complex, so most investors choose to hire an experienced immigration attorney to ensure it is done correctly and completely.
3. Apply for a Conditional EB-5 Green Card
Once USCIS has approved an investor’s I-526 or I-526E application, they are eligible for conditional permanent resident status.
- Investors already living in the United States must submit Form I-485 to USCIS.
- Investors living outside of the United States must submit Form DS-260 and then attend a visa interview at the U.S. embassy or consulate in their home country.
With the Reform and Integrity Act of 2022, eligible investors living in the United States on non-immigrant visas can concurrently apply for adjustment of status while filing their I-526E petitions. While waiting for their I-485 processing, foreign investors and their families can also apply for work authorization and travel permits.
Once approved, the conditional EB-5 Permanent Resident Card is valid for two years, allowing the investor, their spouse, and their dependents to live in the United States.
4. Fulfill EB-5 Program Requirements
After gaining conditional permanent resident status, the investor must fulfill all EB5 program requirements over the ensuing two-year period. This primarily entails:
- Keeping the required amount of money invested in the commercial enterprise.
- Ensuring that money remains at-risk—in other words, ensuring that it is exposed to potential loss due to market conditions.
- Generating 10 full-time jobs for U.S. workers.
- Being involved in running the business. The minimum requirement is to have a policy-making role.
How the job creation requirement is measured differs for direct vs. regional center investments:
- Direct investors: Only full-time jobs directly created by the new commercial enterprise may be counted.
- Regional center investors: May count both direct and indirect jobs, as well as induced jobs. Indirect jobs are those created as a result of the economic activity stemming from the new commercial enterprise. Induced jobs are those created in the local community as a result of increased consumer spending by employees of the NCE and by other businesses benefitting from the activities of the commercial enterprise. These indirect and induced jobs are estimated using economic modeling.
5. File Form I-829
Within 90 days before the end of the two-year conditional permanent resident status period, the EB-5 investor must file Form I-829. Upon approval of the I-829 petition, the immigrant investor will be granted permanent resident status, at which point they, along with their spouse and dependents, will receive their EB-5 Permanent Resident Card.
To successfully file an I-829 petition, the applicant must present several supporting documents to USCIS as evidence that they have successfully met all requirements of the EB-5 program and qualify for the removal of conditions on their permanent resident status.
The documentation that applicants must submit includes:
- Evidence of conditional permanent resident status, which may include a copy of the EB-5 investor’s conditional Green Card and any other relevant immigration documents.
- Evidence related to the investor’s commercial enterprise, investments, and job creation (e.g., financial statements, tax returns, invoices, contracts, etc.).
- Evidence for petitioners filing as a former spouse or as a spouse or child whose EB-5 investor spouse or parent has died.
- Evidence of any criminal history.
How Long Does It Take to Get an EB-5 Green Card?

The total time required to obtain an EB-5 Green Card varies depending on a number of factors, including:
- The type of project the individual invests in
- USCIS processing efficiency
- EB-5 visa demand from an immigrant’s home country
- How straightforward or complex an individual’s case is
- How thoroughly their forms have been submitted
- The level of evidence provided to demonstrate compliance with all EB-5 program requirements
Permanent Resident Status Rights and Responsibilities
Permanent resident status entails certain rights and responsibilities, which are outlined below.
Rights of Permanent Residents
U.S. permanent resident status grants immigrants many rights and privileges, including:
- Living and working anywhere in the United States: Permanent residents can live and work anywhere in the United States. However, it is important to consider that during the conditional residency period, it is recommended for direct investors to remain near their commercial enterprise to effectively manage its day-to-day operations.
- Full protection under federal, state, and local law: Permanent residents are entitled to full legal protection under U.S. laws, including access to the court system and due process rights.
- Freedom to travel abroad: Permanent residents can still use a valid passport issued by their home country.
- Access to the United States’ world-class education system: Permanent residents can send their children to public grade school, as well as access the country’s renowned universities and colleges. Some permanent residents may be eligible for federal financial aid programs for higher education, and some may be eligible for in-state tuition rates at public universities and colleges.
- Potential access to the Social Security and Medicare benefits: After meeting certain eligibility criteria, permanent residents may be eligible to receive Social Security benefits and Medicare health coverage.
- A path to U.S. citizenship: EB-5 Green Card holders have the option to apply for citizenship through naturalization five years after becoming permanent residents. The two-year conditional residency period also counts toward this time requirement.
Responsibilities of Permanent Residents
Along with the rights and privileges mentioned above, permanent residents are expected to fulfill certain responsibilities, including:
- Paying U.S. taxes: Permanent residents are required to pay all applicable state and federal income taxes. They must file income tax returns with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), paying taxes on both their U.S. and worldwide income. Investors from countries with whom the United States has tax treaties may be able to obtain credit for the payment of their foreign taxes.
- Register with Selective Service: Like all male U.S. citizens between the ages of 18 and 26, male Green Card holders must register with the Selective Service System. Registration for Selective Service does not, in itself, entail service in the U.S. military, but it does mean that they will be subject to the draft if the U.S. government chooses to conscript men into military service.
- Demonstrate good moral character: In addition to paying taxes and registering with Selective Service, permanent residents are expected to be of good moral character. Generally, this involves not committing crimes, giving false testimony, etc.
- Maintain a physical presence: To maintain permanent resident status, an immigrant must fulfill the physical presence requirement, which generally entails physically residing within the United States for six months or more in any given year. If a permanent resident spends more than one year outside of the United States, they must obtain a re-entry permit or face losing permanent resident status.
If an EB-5 investor who has become a permanent resident has been outside of the United States for two or more years after being issued a re-entry permit, they will also need to submit a returning resident (SB-1) immigrant visa. While outside the United States, permanent residents are still required to file U.S. income tax returns, and failure to do so may jeopardize their status as Permanent Resident Card holders. Permanent resident status will be considered abandoned if a Green Card holder moves to another country and no longer intends to reside in the United States.
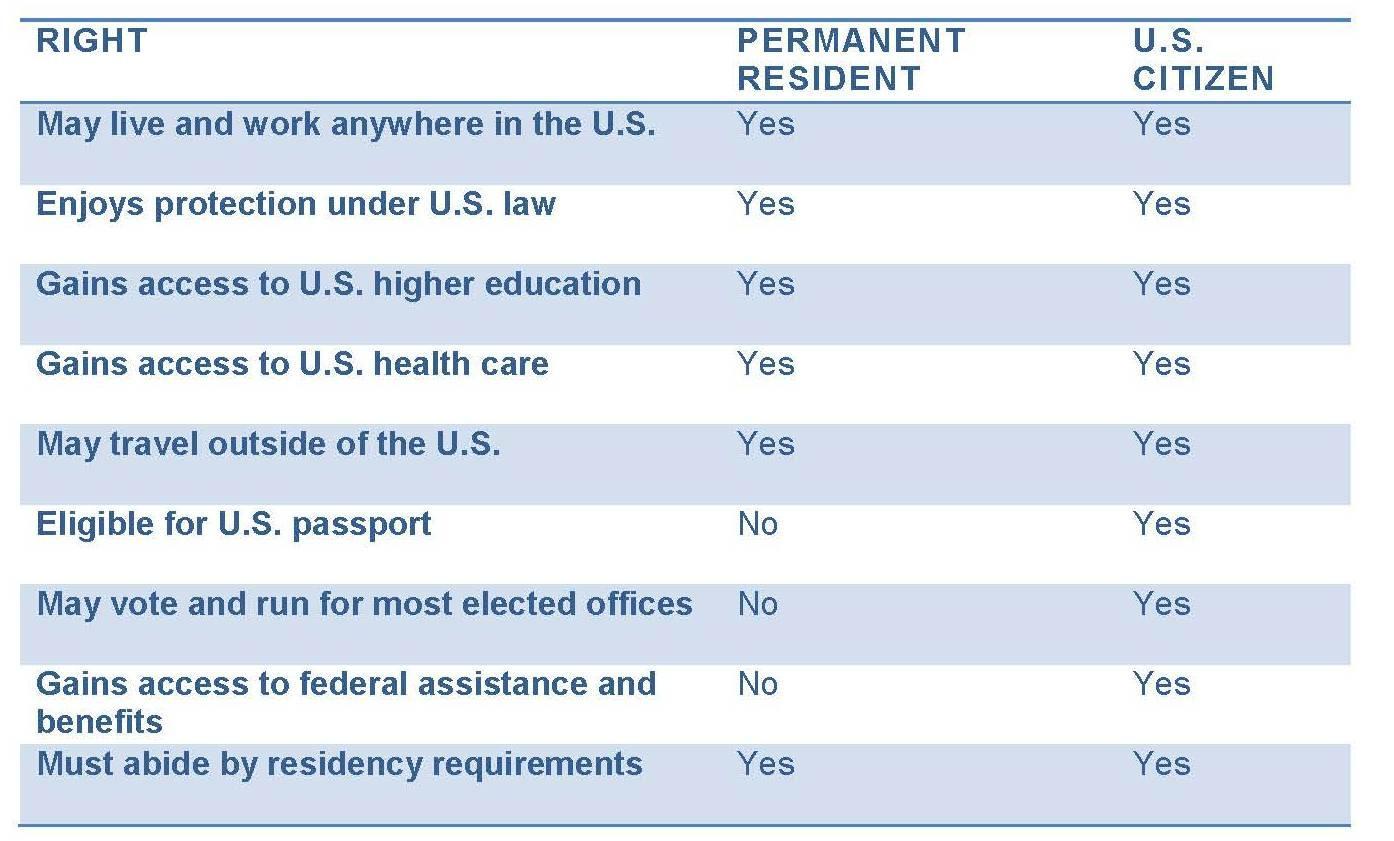
Rights of Permanent Residents and U.S. Citizens Compared

Permanent resident status is not the same as U.S. citizenship. While Permanent Resident Card holders can live and work in the United States, they remain citizens of their home nation. As such, permanent residents cannot:
- Obtain U.S. passports
- Vote in U.S. federal elections
- Run for U.S. federal or most state-level elected office
Additionally, it may be easier for U.S. citizens to bring family members who are foreign nationals into the United States. U.S. citizens also have more access to federal jobs, as well as federal assistance and benefits—including certain access to Social Security and Medicare.
To become a citizen of the United States, a permanent resident must file for citizenship through USCIS.
Despite the differences between the rights of permanent residents and U.S. citizens, Green Card holders are, in fact, entitled to many of the same benefits as U.S. citizens, as can be seen from the table below.
Get Your EB-5 Permanent Resident Card with EB5AN
Obtaining a Green Card through the EB-5 visa is a popular option, but it does involve several stages, each with its own intricacies. That’s why prospective investors are encouraged to work with reputable industry leaders. This helps minimize financial and immigration risks while increasing their chances of success.
EB5AN has helped more than 2,300 families from 60 countries relocate to the United States as lawful permanent residents. Our expert team has more than a decade of experience, and offers clients first-rate, low-risk EB-5 regional center projects with 100% USCIS project approval rate to date.
If you want to obtain an EB-5 Green Card for you and your family, book a call with our EB-5 team today to get help through every step of the process.










