EB5AN State of New York Regional Center
Geographic coverage: Multiple counties in the State of New York
View the official regional center designation letter for the EB5AN New York Regional Center.
Contact us now to learn more about becoming a business affiliate.

Benefits of Affiliation with our New York EB-5 Regional Center
Immediate Ability to Raise EB-5 Capital in New York
Business affiliates of EB5AN, including our New York EB-5 regional center, can immediately begin raising EB-5 investment funds in any of the designated geographic areas that comprise our USCIS-approved regional centers.
Indirect Job Creation Calculations
Business affiliates of our regional centers can calculate job creation through both direct and indirect job methodologies. This leads to higher job creation figures than direct non-regional center calculations of actual payroll employees.
Regional Center Affiliation Process
The regional center affiliation process can be a fast solution and a great fit for those looking to begin a project immediately. The benefits of affiliating with a regional center make this an excellent choice for many project developers.
Our experienced team will work with you to understand whether EB-5 funding is a good fit for your project and whether you qualify to affiliate with our regional centers.
Let Us Help You to Create Your Own New York EB-5 Regional Center
Our Team Will Complete Your I-924 Application for a New York EB-5 Regional Center in Three Weeks
EB5AN has obtained full state regional center coverage in multiple states and has completed more than 100 USCIS-compliant business plans and economic impact studies. The I-924 application process is complicated and requires legal expertise, economic analysis, business plan creation, and an understanding of how USCIS adjudicates applications.
EB5AN has the internal resources to assemble all required aspects of an I-924 application. Additionally, we have extensive experience with I-924 applications and understand all the key components and common pitfalls.
There are various approaches to take when filing an I-924 form; please contact us to learn more about the process and how we can work together to get your regional center approved quickly by USCIS.
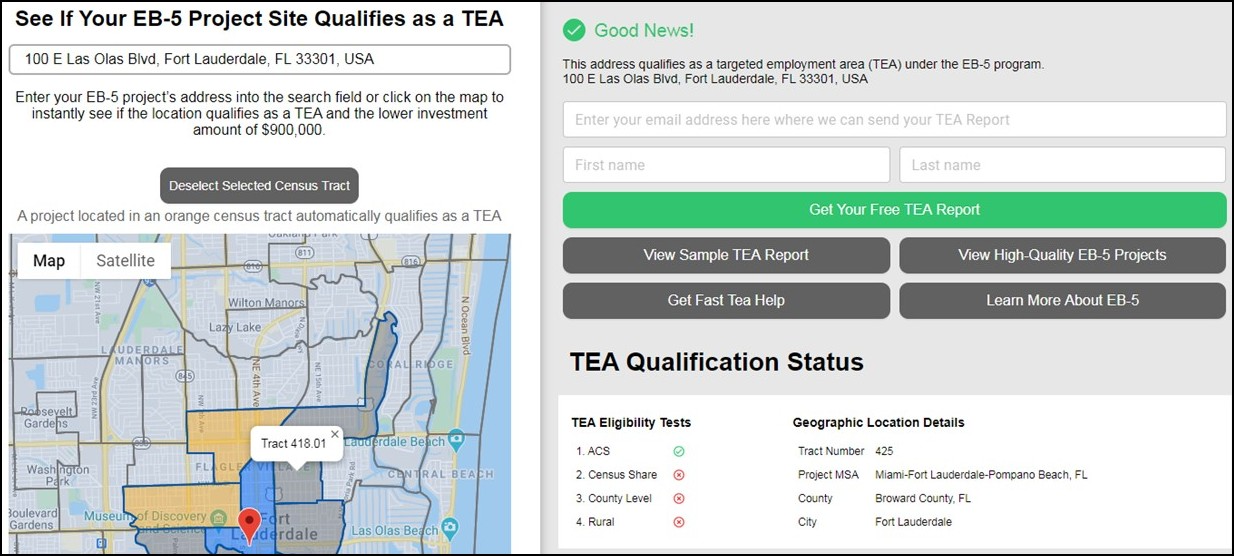
Targeted Employment Area (TEA) Qualification Report in New York for EB-5 New York Regional Center Projects
Please visit our EB-5 TEA Map to determine whether your New York EB-5 regional center project’s location qualifies as a rural or high unemployment targeted employment area (TEA).
Free Targeted Employment Area Map for all 50 States
Click image to view the TEA map and instantly download a free TEA qualification report.

![]()
Because TEA designation is crucial to the success of many EB-5 projects, it is important to understand how USCIS reviews TEA designation requests. Once you determine whether your New York EB-5 regional center project is located in a TEA, you can prepare a TEA report yourself. The free downloadable report available through the EB5AN TEA map is also suitable for submission to USCIS.
If you still need assistance with preparing your EB-5 TEA report for your EB-5 regional center project in New York, please contact the EB5AN team directly by phone at 1-800-288-9138 or via e-mail at info@eb5an.com, or simply order an EB-5 TEA Qualification Report.
About the State of New York and the Economic Climate of our EB-5 New York Regional Center
The EB5AN New York EB-5 regional center was created to provide an investment vehicle for qualified foreign investors seeking to obtain permanent resident status in the United States through an investment in a USCIS-approved EB-5 regional center with geographic coverage of multiple counties in the State of New York.
Historically, several elected New York public officials, including senators and congressional representatives, have endorsed the EB-5 regional center program as a great opportunity for the U.S. economy and for foreign investors who want to immigrate to the United States and invest in a USCIS-approved New York EB-5 regional center such as the EB5AN New York Regional Center.
New York: Population and Income Demographics
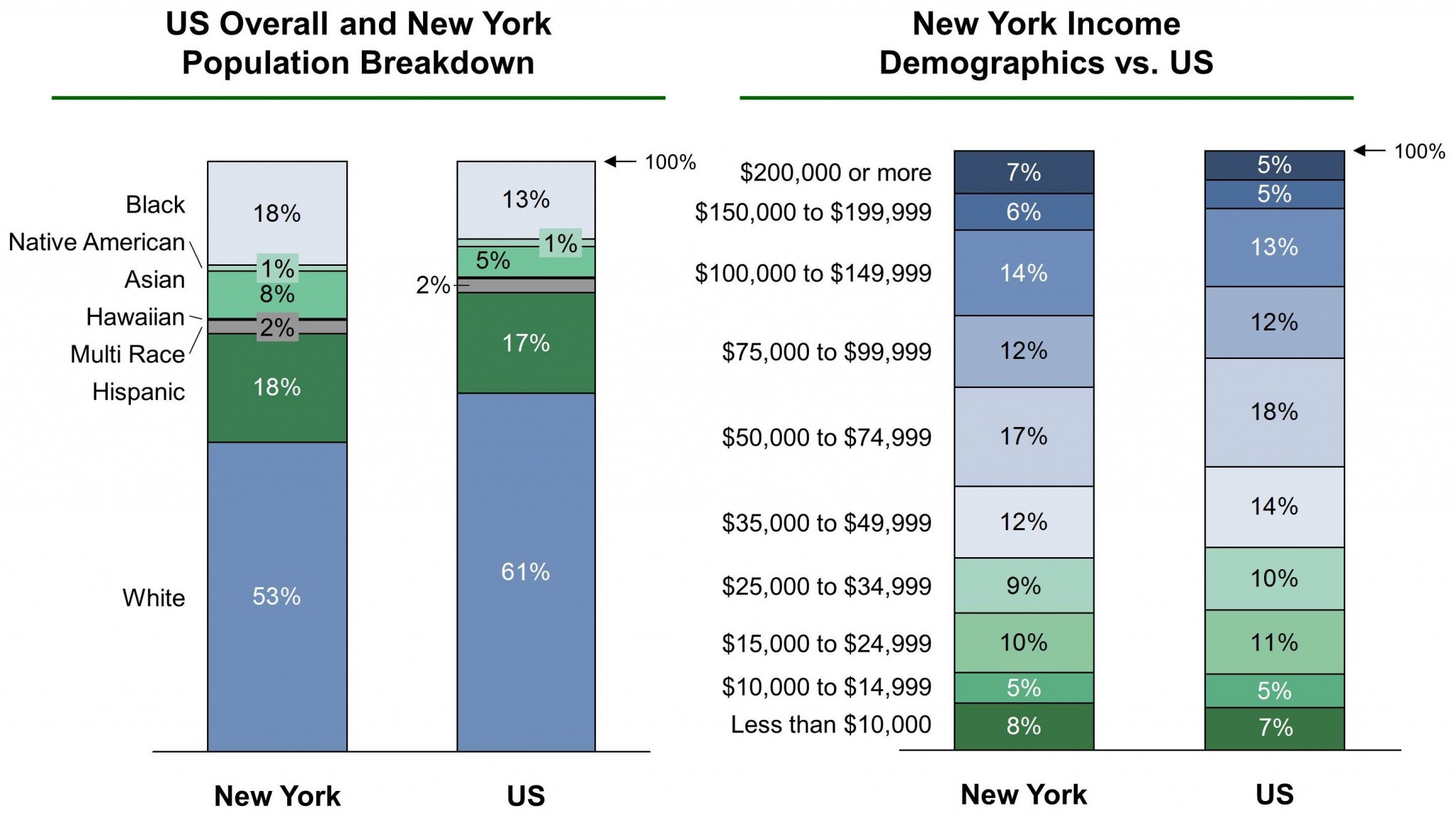
According to the 2010 U.S. Census, New York State has a population of approximately 15.7 million people over the age of 16. Of this, there are approximately 10 million people in the labor force, with 9 million who are employed and 921,000 who are unemployed. These population numbers represent approximately 7.2 million households.
New York: Unemployment Trends
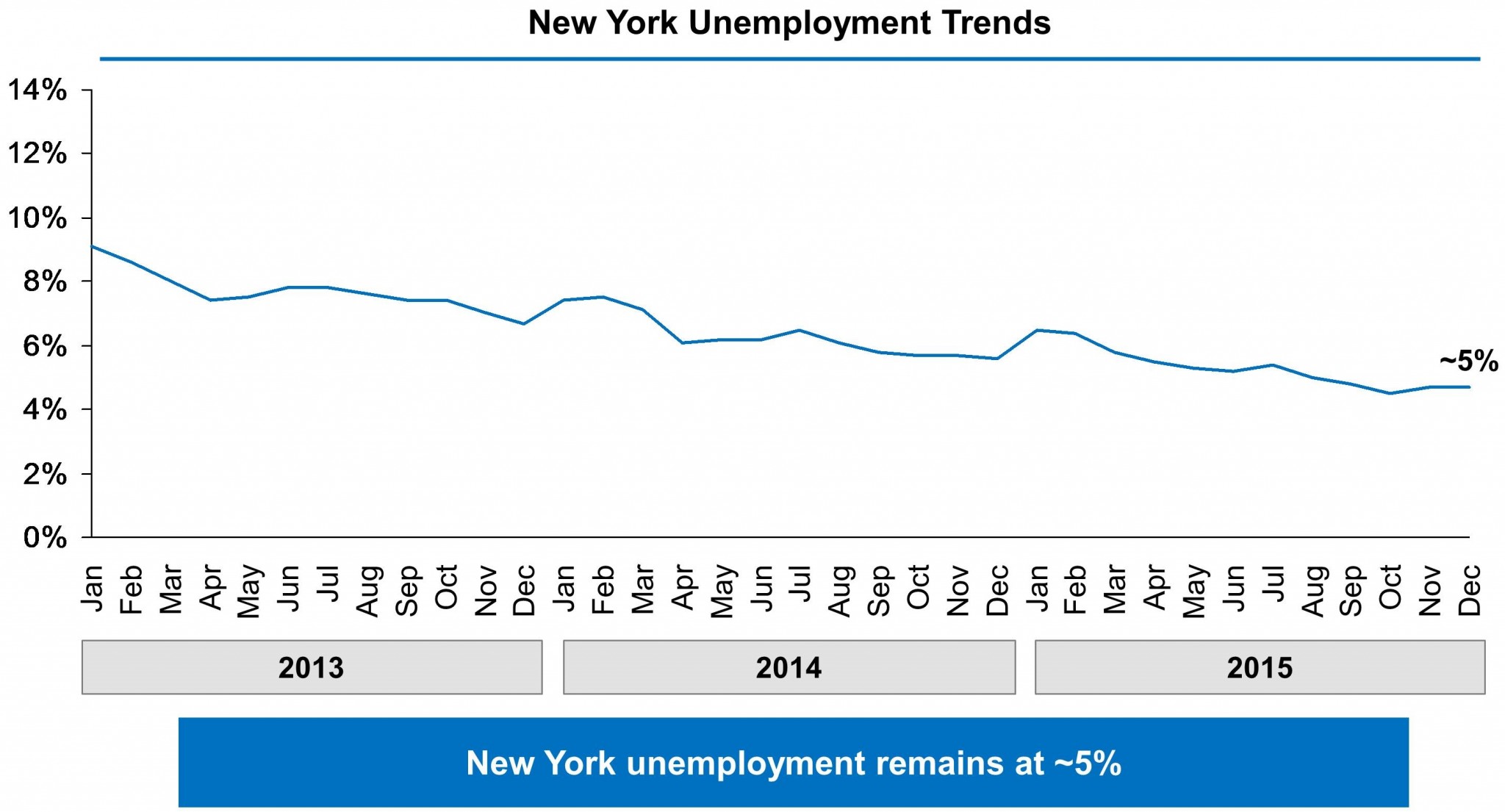
Unemployment statistics for 2015 show average unemployment in New York State at 5.3%. Monthly unemployment rates were 4.5% for October 2015, 4.7% for November 2015, and 4.7% for December 2015.
The State of New York covers an area of 54,555 square miles, with a width of 285 miles and a length of 330 miles. This implies a population density of 417 people per square mile, which makes New York the seventh-most densely populated state in the United States.
The capital of New York is Albany, the largest city is New York City, and the largest metro area is the New York City metropolitan area. The gross domestic product (GDP) of the state of New York in 2010 was $1,160 billion. This implies a compound annual growth rate from 2000 to 2010 of 4.17% and a per capita GDP of $53,377. New York State has the third-largest economy in the United States by GDP.
Anchored by Wall Street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan, New York City has been called both the most economically powerful city and the leading financial center of the world, and Manhattan is home to the world’s two largest stock exchanges by total market capitalization, the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ, respectively. Many of the world’s largest media conglomerates are also based in the city.
Albany, Saratoga County, and the Hudson Valley are major centers of nanotechnology and integrated microchip circuit manufacturing, while the Rochester area is important in the field of photographic processing and imaging. New York State also has a large manufacturing sector that includes printing and the production of garments, furs, railroad equipment, and bus line vehicles; many of these industries are concentrated in Upstate regions.
New York is a major agricultural producer, ranking among the top five states for agricultural products such as dairy, apples, cherries, cabbage, potatoes, onions, and maple syrup. New York State is the largest producer of cabbage in the U.S. The state, which has about a quarter of its land in farms, produced $3.4 billion in agricultural products in 2001. The south shore of Lake Ontario provides the right mix of soils and microclimate for many apple, cherry, plum, pear, and peach orchards. Apples are also grown in the Hudson Valley and near Lake Champlain.
New York State Government & EB-5 Investment Financial and Employment Statistics
New York: Real GDP (2011–2014)
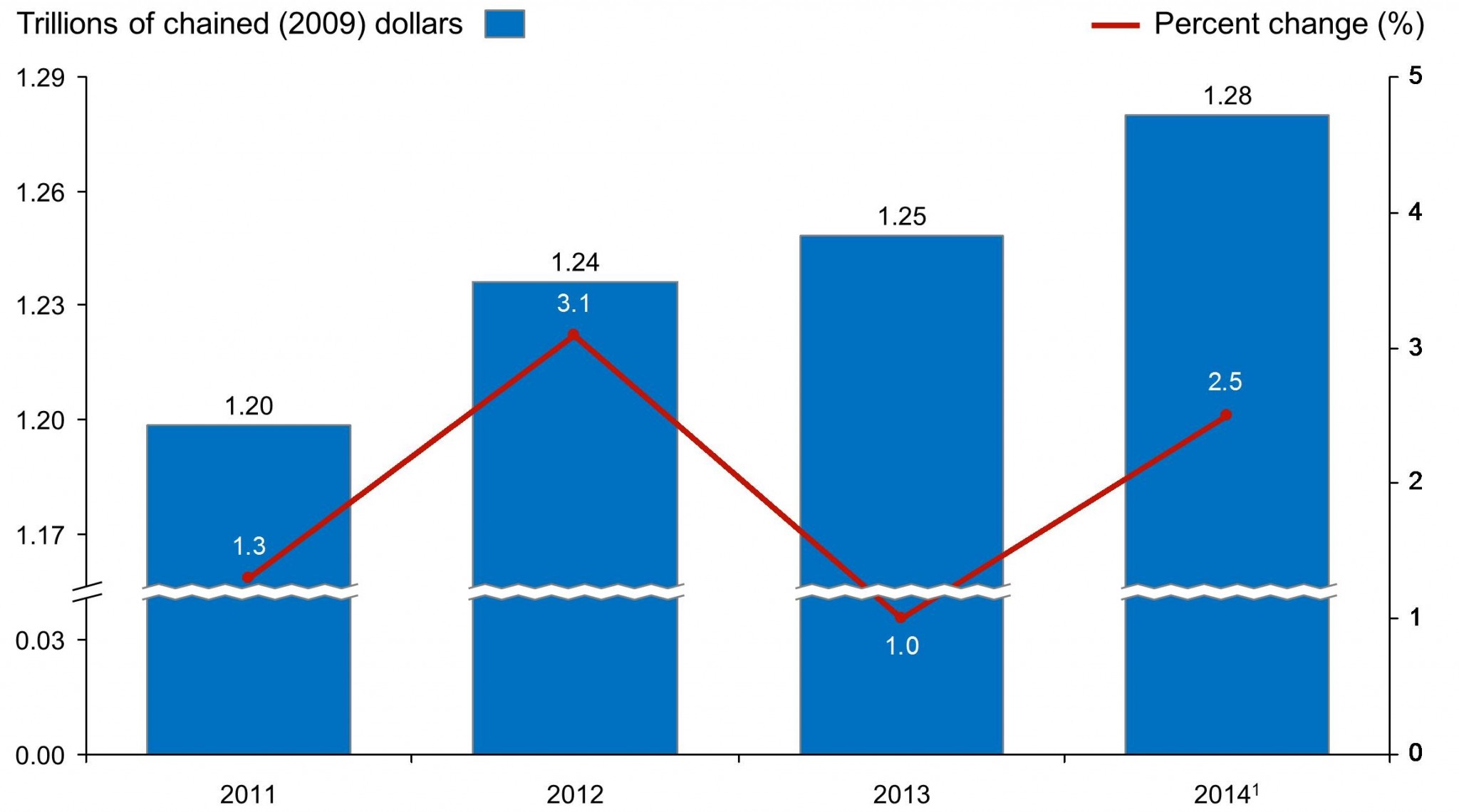
From 2011 to 2014, New York’s GDP grew by 6.67%, with an average annual GDP growth of 1.98%. In 2014, New York’s real GDP was $1.28 trillion, ranking third in the U.S. The 2011–2012 financial year saw the largest percent change in GDP at 3.1%, signaling a strong and growing economy.
New York: Total Personal Consumption Expenditure (2012–2014)
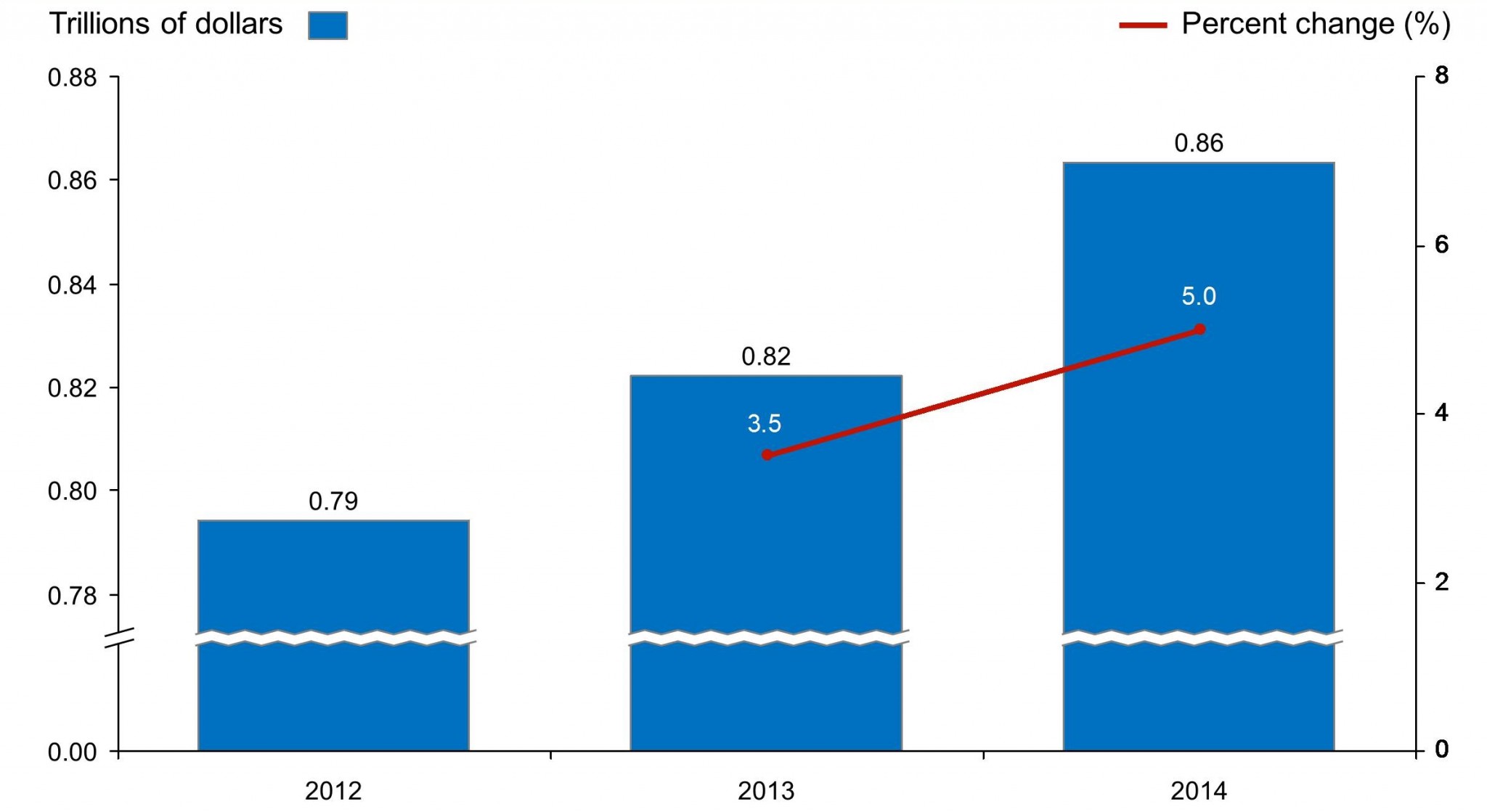
Personal consumption expenditure is the primary measure of consumer spending on goods and services and is a primary engine driving economic growth. New York’s personal consumption expenditure grew from $0.79 trillion in 2012 to $0.86 trillion in 2014. From 2013 to 2014, total personal consumption expenditure grew by 4.9%.
New York: State government finances (2013)
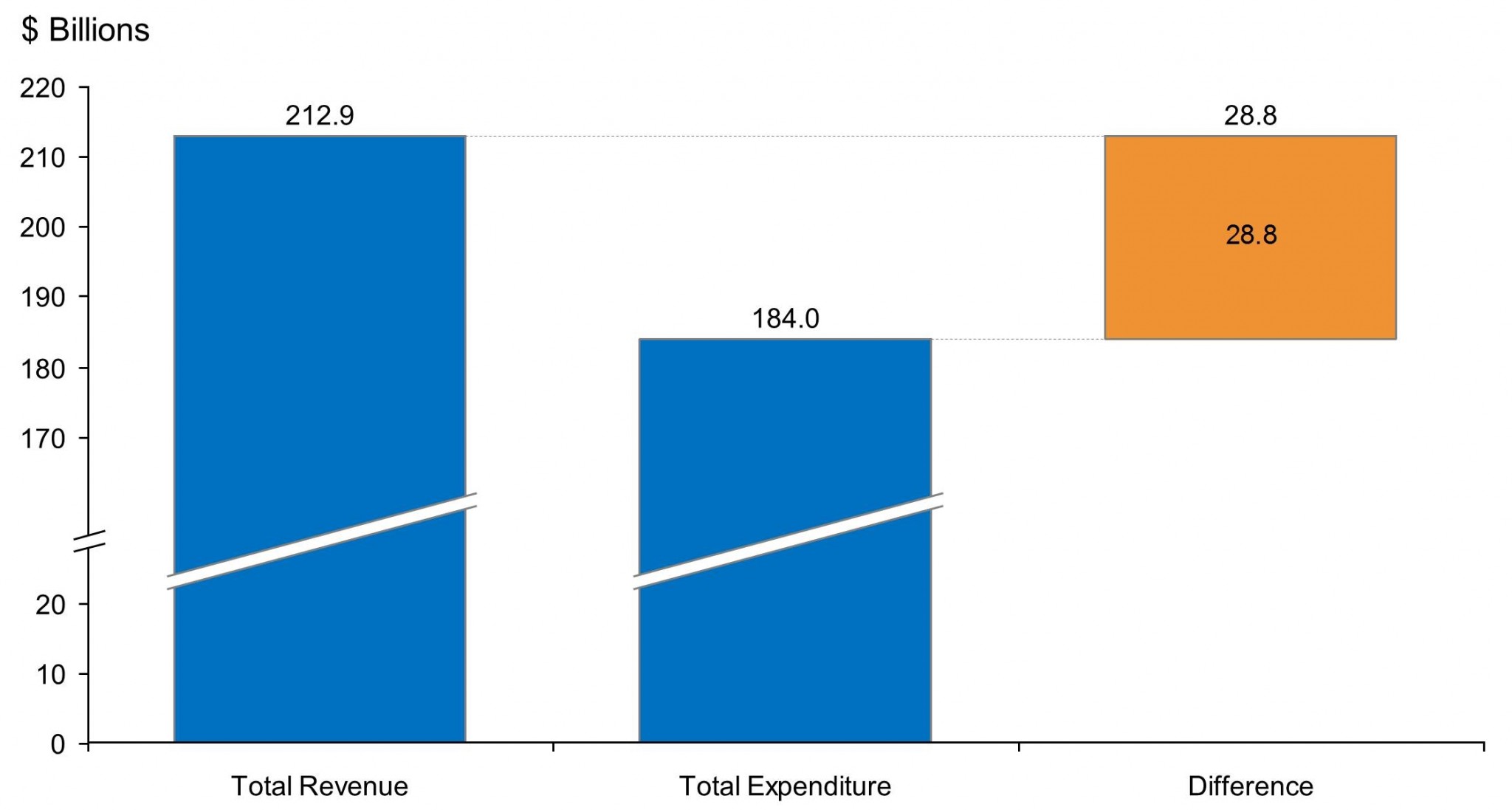
In 2013, the government of New York collected $212.9 billion and spent $184 billion, resulting in a net difference of $28.8 billion. Revenue is sourced from federal and local taxes, sales tax, and individual and corporate taxes. Expenditures include education, welfare, highways, police, and other social services.
New York: Total economic impact of EB-5 investments (2013)
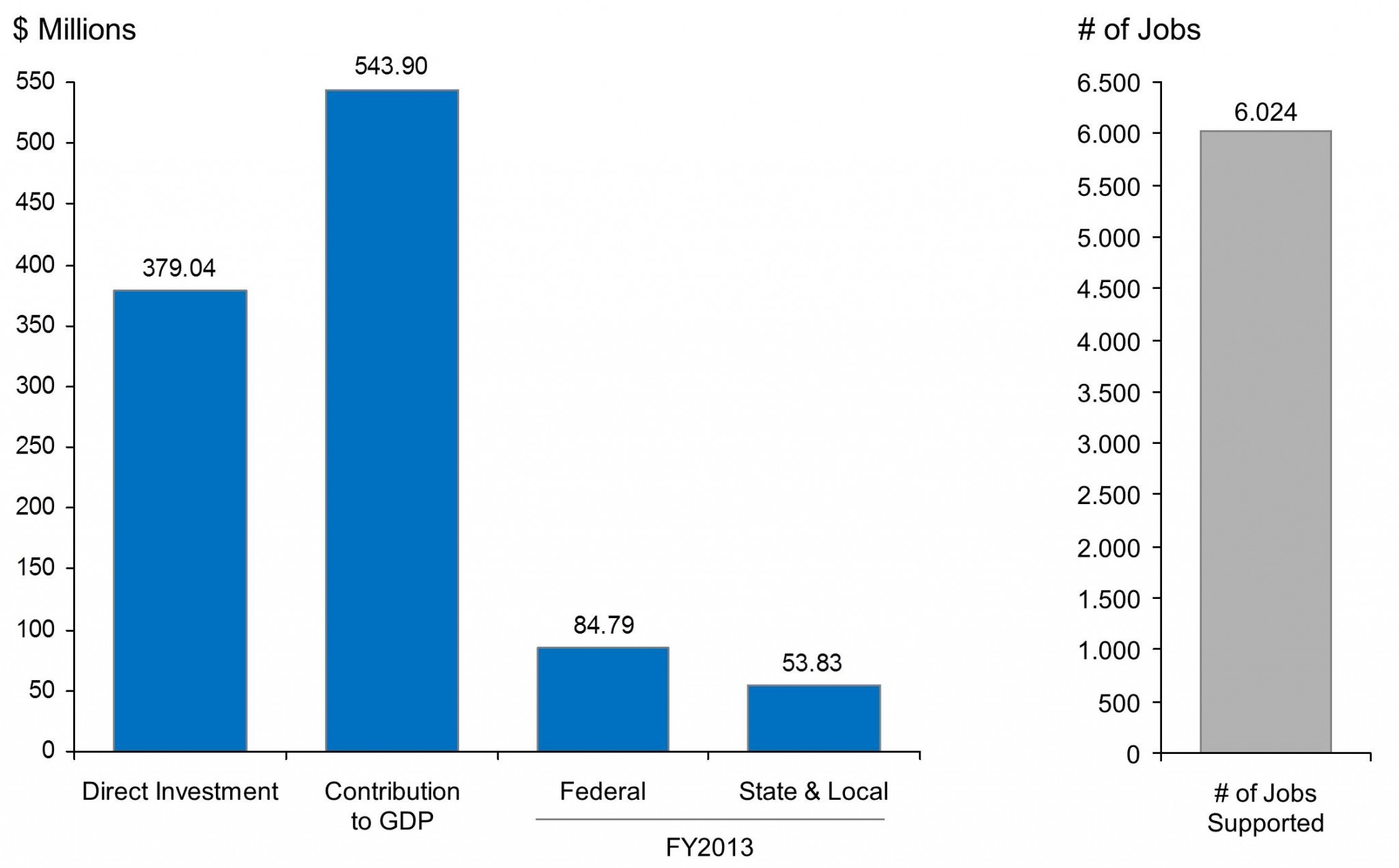
In New York, EB-5 investment has supported the direct creation of 6,024 jobs. These jobs were the result of roughly $379 million in direct investment from EB-5 projects, contributing $543.9 million to the state’s GDP. EB-5 investment in New York also contributed $84.79 million to federal revenue and $53.83 million to New York state government and local municipal revenue.
New York: New Privately Owned Housing Units Authorized by Building Permits in Permit-Issuing Places
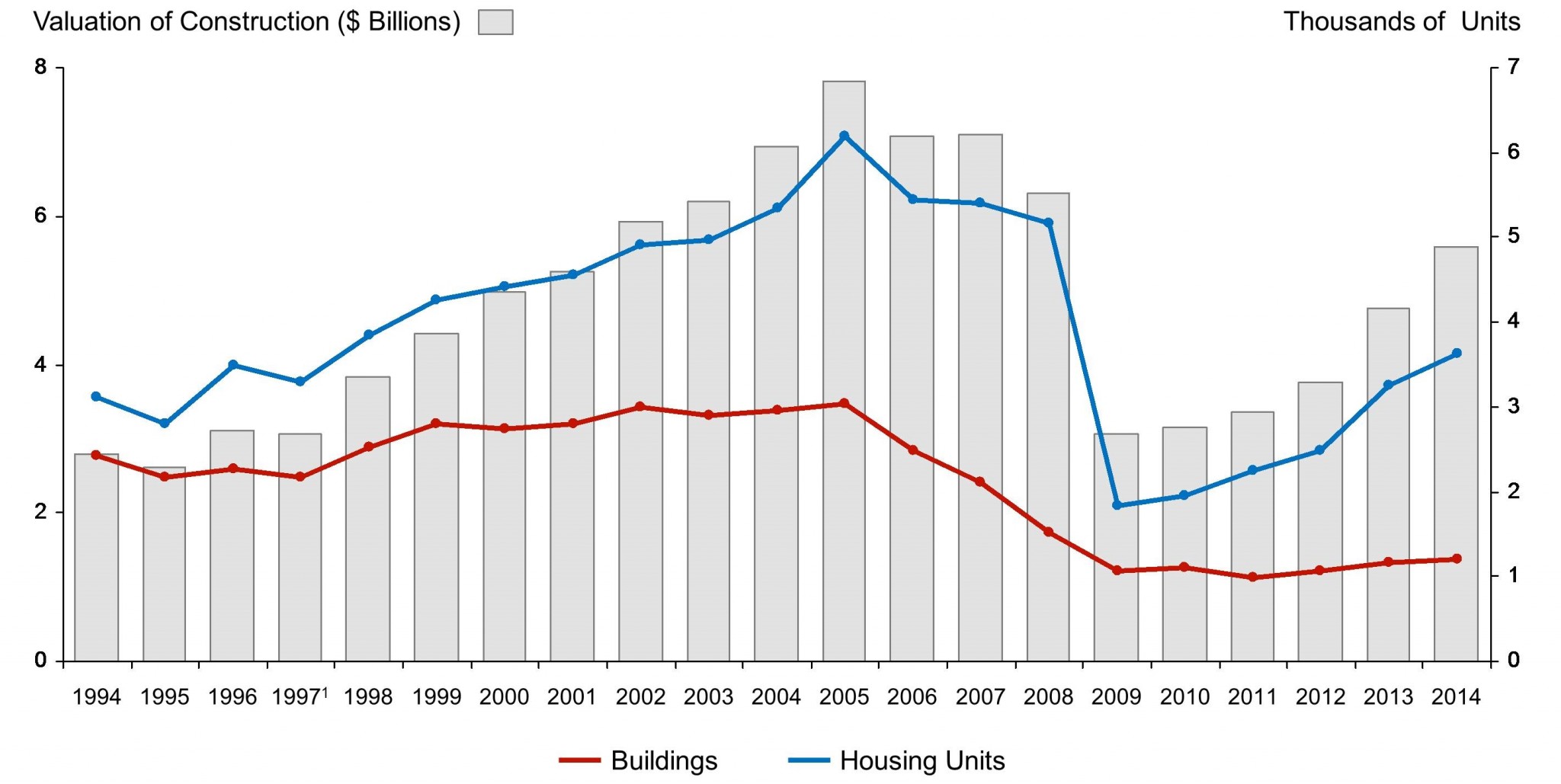
Since 2009, New York has seen increased growth of privately owned housing units, both in new buildings and housing units. In 2014, roughly 5,000 privately owned units were authorized by building permits. Most of these units are in New York’s largest cities, which include New York, Brooklyn, Borough of Queens, Manhattan, and Bronx.
The EB5AN State of New York Regional Center covers the entire state of New York, including the following cities in the state. New York is the most populous city in the United States and a center for media, culture, food, fashion, art, research, finance, and trade. The city of Buffalo is undergoing a dramatic transformation as its proud history and incredible architectural legacy weave their way into every aspect of a renewed civic life. Rochester lies south of Lake Ontario and sits on the Genesee River and historic Erie Canal.
Flushing is a large commercial and retail area and the fourth-largest central business district in New York City. Jamaica is an expansive neighborhood located in eastern Queens and home to an extremely diverse array of peoples and cultures. Elmhurst is a working- or middle-class neighborhood in the borough of Queens. Astoria is a multicultural neighborhood of low-rise residences and small businesses known for its Greek tavernas and cafes; the area is home to a variety of traditional ethnic eateries and trendy spots. Queens Village is a mostly residential middle-class neighborhood in the eastern part of the New York City borough of Queens.
Woodside is a residential and commercial neighborhood filled with restaurants and pubs from a variety of cultures. Yonkers is the fourth-most-populous city in the state and is known as the “City of Seven Hills,” namely Park Hill, Nodine Hill, Ridge Hill, Cross Hill, Locust Hill, Glen Hill, and Church Hill. Richmond Hill is a commercial and residential neighborhood known as Little Guyana–Trinidad and Tobago. New Hyde Park is a village in Nassau County, which is split between the towns of Hempstead and North Hempstead. Jackson Heights is a neighborhood in the northwestern portion of the borough of Queens, and Glen Oaks is a neighborhood in the easternmost portion.