
The EB-5 Program is one of the most popular methods to obtain funding for a property development project in the United States. However, structuring your EB-5 project correctly is essential for ensuring a successful application.
Navigating the different structural methods of an EB-5 project can become overwhelming, especially if you’ve never done it before or don’t have any prior experience.
In this article, we compiled a list of important components that you should consider when structuring your EB-5 project.
Who Is Involved in an EB-5 Project?
EB-5 Project Structuring: Types of Investment
EB-5 Project Structuring: Roles and Responsibilities of Involved Parties
Structure Your EB-5 Project for Success with EB5AN
Frequently Asked Questions about EB-5 Projects
If you are planning on starting an EB-5 project, read on to understand the roles and responsibilities of the different key players involved, including the role of the project developers, which allow you to set yourself up to create a successful EB-5 project.
Who Is Involved in an EB-5 Project?

The first step in any project structuring discussion is to understand the parties involved in the transaction and to determine which roles they will play. Participants may have several responsibilities, so it is critical to consider the impact of the different parties and the specific roles they fulfill.
Usually, the parties involved in an EB-5 transaction include:
- Project sponsor: An entity that initiates and manages the business project that requires an EB-5 investment. These projects often include real estate development projects or similar enterprises.
- Preferred equity sponsor: This is an equity investor or manager who controls and coordinates the funding of an EB-5 project. They are usually the same entity as the project sponsor or appointed by the project sponsor.
- Regional center sponsor: This entity is responsible for overseeing EB-5 projects in a specific geographical area designated for development by United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). These areas typically require an economic boost through job creation and investments.
- EB-5 fund manager: The EB-5 fund is typically structured as a limited partnership or LLC, with investors serving as limited partners or members. Fund managers serve as general partners or managing members of the EB-5 fund.
Project advisors can also be involved in EB-5 deals. These advisors can include individuals with legal, financial, or technical expertise who can provide guidance to help ensure the project’s success, such as:
- Immigration attorney: A lawyer who specializes in EB-5-related matters can help investors prepare and file any required documents, petitions, and applications. This ensures that foreign investors comply with U.S. immigration laws while going through the process of obtaining citizenship.
- Securities attorney: These individuals are responsible for ensuring that the EB-5 investment complies with U.S. securities laws and regulations. They help draft offering documents and ensure that investors receive the required communications.
- Business plan writer: This person helps a foreign investor write a comprehensive business plan for their project. These plans highlight objectives, financial projections, and job-creation estimates, which are critical for EB-5 petition approval.
- Economist: An economist plays a crucial role in an EB-5 deal because they conduct economic impact studies. This assesses the project’s potential for creating jobs and generating economic benefits within the targeted employment area (TEA)—two components that are vital for the EB-5 application process.
- Bank/escrow service advisors: These institutions are responsible for holding and managing EB-5 investor funds in escrow until specific conditions are met—such as USCIS approval of certain petitions. Once these conditions have been satisfied, the money is released to the project.
Below is a chart that helps illustrate the different roles involved in an EB-5 project. This chart also covers the responsibilities of each roleplayer to help you map out an effective business and legal structure for the project.
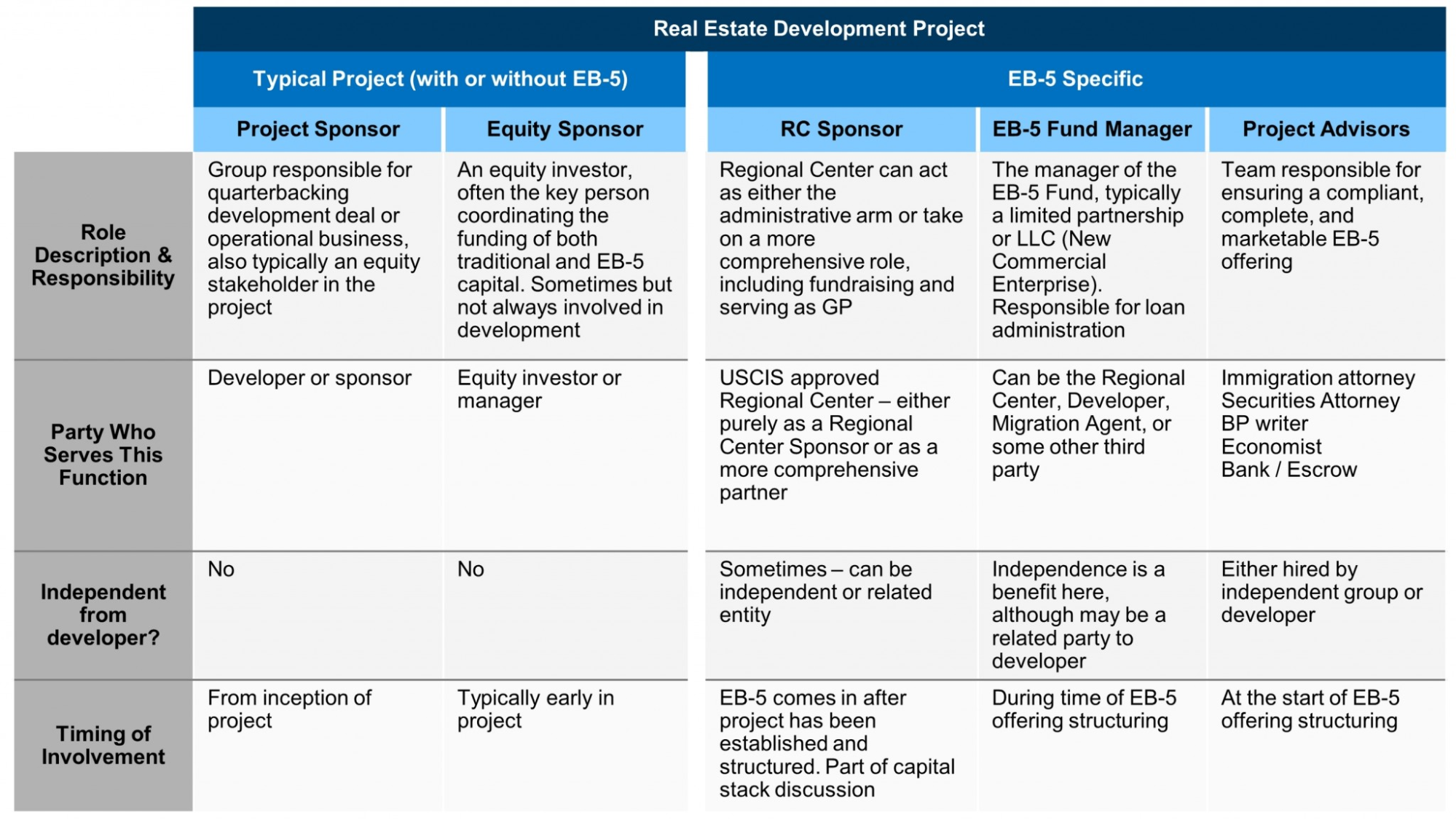
Download our free EB-5 project entity chart and roles framework in an editable PowerPoint format.
Download Editable Project Entity Chart & Roles Framework
EB-5 Project Structuring: Types of Investment

When structuring your EB-5 project, it’s important to first determine whether the investment you receive will function as a loan amount or equity investment.
EB-5 investors will always have some form of equity ownership, either directly in a project or in an EB-5 fund. This fund is often structured around a new commercial enterprise (NCE) and allows investors to make a loan to a development company—also known as the job-creating entity (JCE)—or to fund a qualifying business by means of a direct equity investment.
The most common structure that EB-5 funds tend to favor when investing in an EB-5 project is a loan or debt investment. This structure offers better standardization and protection to investors, including a clear exit strategy should the project fail.
If the investment is structured as a loan, the NCE can use different types of debt agreements, each with its own rules and obligations—including a senior loan, second position loan, or mezzanine loans.
It is also possible to structure equity investments in various ways, but this needs to be project-specific and will depend on the investors’ needs, including their expectations of return, and the position of the EB-5 capital in the capital stack.
A qualified securities attorney can help you make these decisions and ensure that your project is set up legally.
Equity investment structures:
- Traditionally used in smaller deals where EB-5 owners are directly involved in management or want meaningful returns on investments.
- Some historic deals may have relied more heavily on the equity model before the loan model became more common.
Debt investment structures:
- Many investors prefer this structure because it’s a more secure form of investment. The typical EB-5 investor’s top priority is to secure a green card, and this method ensures capital preservation.
- Debt instruments are often secured by collateral and have priority over any equity in the project.
- There is a clear path to exit since debt instruments have a maturity date.
- The loan structure allows for more standard terms, covenants, and obligations.
- The EB-5 fund enjoys various privileged rights with respect to the development of projects.
EB-5 Project Structuring: Roles and Responsibilities of Involved Parties
After the structure of the investment is determined, the team can begin to decide the roles and allocate the responsibilities of the involved parties. A typical business composition may look similar to the one we detail below, where we use a mezzanine loan structure as an example:
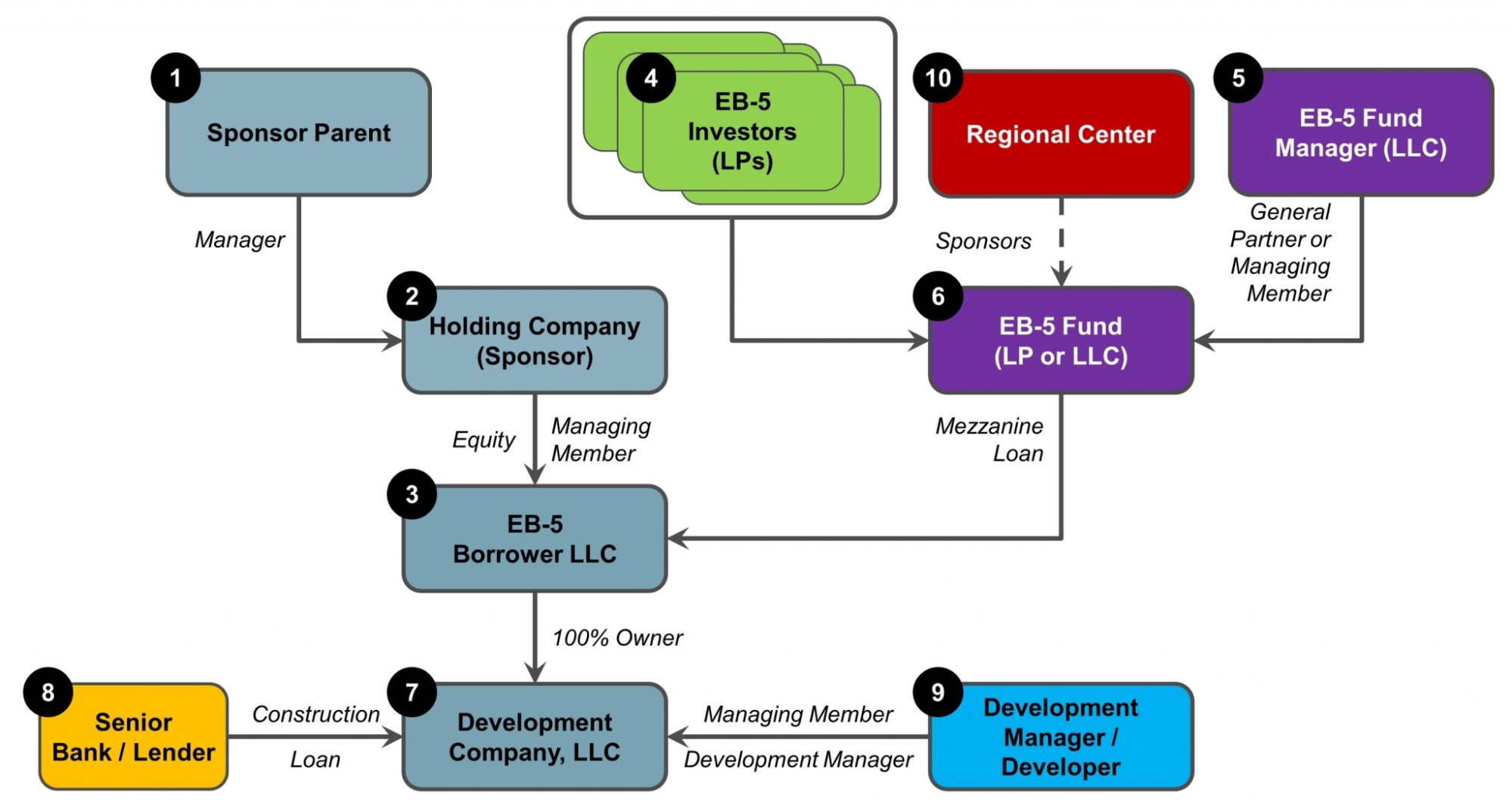
Download Editable Project Entity Chart & Roles Framework
- Sponsor parent: The sponsor parent is usually the manager of the holding company. For a larger developer, a sponsor parent represents the company’s recognizable name. Although a sponsor parent can also be the owner of a project, this is rare. These entities—sponsor parent and holding companies—are usually kept separate to limit the liability of the sponsor and protect their financial interests. For example, if a holding company were to go bankrupt, this wouldn’t affect the sponsor parent’s other projects. However, if they were the same entity, bankruptcy could jeopardize all of their other projects.
- Holding company: This company is also referred to as the project sponsor and this entity has ownership of the development/project. A holding company is the entity that owns the EB-5 borrower. Typically, holding companies contribute to developer equity—or funds that help develop the project—within the business.
- EB-5 borrower: This entity is specifically formed for the project, and its purpose is to borrow capital from the EB-5 fund. A new EB-5 borrower will typically be formed for each new project and will be specific to that deal.
- EB-5 investors: Individual EB-5 investors invest in the EB-5 fund by purchasing equity interests. The combined interests of these investors are pooled to form the project fund.
- EB-5 fund manager: This person is responsible for the financial administration of the EB-5 fund. The manager will serve as its general partner if the EB-5 fund is a limited partnership. If the EB-5 fund is an LLC, the individual serves as the managing member or manager of the LLC. The EB-5 fund manager may be affiliated with regional centers or the development company, or be completely independent. The EB-5 fund manager is usually responsible for looking out for the best interests of the investors in the project fund. If the manager is connected to the development company, they have to inform investors of any conflicts of interest.
- EB-5 fund: Contributions from EB-5 investors are pooled into this fund, which is then invested in the project’s development company. Depending on the fund structure, investors purchase partnership or equity interests and may have varying levels of involvement.
- Development company: This company directly owns the project’s assets and typically borrows senior construction loans. It secures loans against the project’s assets.
- Senior bank/lender: Structured debt deals often involve a senior bank or lender with first priority on the project’s assets. They may have an inter-creditor agreement with the EB-5 fund.
- Development manager/developer: This entity manages project development tasks, such as construction and landscaping, often as the manager of the development company.
- Regional center: A regional center program has an administrative agreement with the EB-5 fund. It may be affiliated with the fund manager but this is a service relationship, not ownership. In some cases, the development company may own the regional center, which requires disclosure and conflict identification.
Structure Your EB-5 Project for Success with EB5AN

The EB-5 Program offers a clear path to obtaining a valid green card for investors and their qualifying family members. However, structuring your project correctly to ensure success can be challenging.
Our team of experienced immigration attorneys is ready to help you streamline your visa application to ensure a smooth start for your journey to U.S. citizenship.
Contact EB5AN today to learn how you can become an EB-5 investor and protect your investment funds while successfully completing the immigration process.
Frequently Asked Questions about EB-5 Projects

What is the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program, and how does it work?
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program offers investors a way to become permanent residents in the U.S. by making a qualifying investment in a new commercial enterprise. The program aims to stimulate the U.S. economy by creating jobs through these foreign investments.
What is the minimum capital investment required for an EB-5 project, and where can I invest?
The minimum investment required for an EB-5 project depends on the location of the project. An investor must invest around $1,050,000 million.
However, if the project is located in a TEA—which is either a rural area or an area with high unemployment—the minimum investment is reduced to $800,000. Which is why most investors choose TEA projects.
Investors can also choose to invest directly in a new commercial enterprise (NCE), which requires them to create a minimum number of jobs for qualifying U.S. workers. They must also meet other EB-5 program requirements when making their investment.
What are the job creation requirements, and how are jobs counted in an EB-5 project?
EB-5 projects must create or preserve a certain number of full-time jobs for qualified U.S. workers. Generally, an investment must create at least 10 jobs per investor.
The jobs created by immigrant investors in TEA projects can be direct, indirect, or induced. Direct jobs are those created within the commercial enterprise itself. Indirect jobs result from the investment’s impact on other businesses, while induced jobs are created when employees spend their wages in the local economy. For direct investments, only direct jobs count toward the job creation requirement.
Job creation is a critical aspect of EB-5 projects and is typically documented and verified during the immigration process.
What are the potential risks and benefits of investing in an EB-5 project?
Investing in an EB-5 project offers the potential benefit of obtaining U.S. permanent residency for the investor and eligible family members. It also provides an opportunity for a return on investment if the project succeeds.
However, there are risks to consider. These may include the possibility of capital loss if the project fails, changes in immigration policies, and the need to meet strict program requirements.
Performing due diligence, carefully selecting projects, and working with experienced professionals are crucial to mitigate risks and maximize the potential benefits of an EB-5 investment.
Do EB-5 investors get their money back?
EB-5 investors have the potential to get their money back, but it depends on several factors related to the specific EB-5 project:
- Return of capital: Typically, EB-5 investors’ capital is at risk because it’s invested in an NCE. However, after a certain period—often around five years when the investor’s immigration status is granted—the invested capital is eligible for return.
- Return on investment: In addition to the return of their capital, investors may also receive a return on their investment if the EB-5 project generates profits. This return is not guaranteed and depends on the project’s success and profitability.
- Risks and variables: It’s essential to understand that EB-5 investments carry inherent risks. If the project faces financial difficulties or fails to create the required jobs, investors may not receive their full investment back.
- Project selection: The likelihood of getting money back largely depends on the EB-5 project chosen. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence and work with experienced professionals to select projects with a strong track record and a solid business plan.
- Timing: The timing of capital return can vary from project to project and may be influenced by USCIS approval and immigration processing times.











